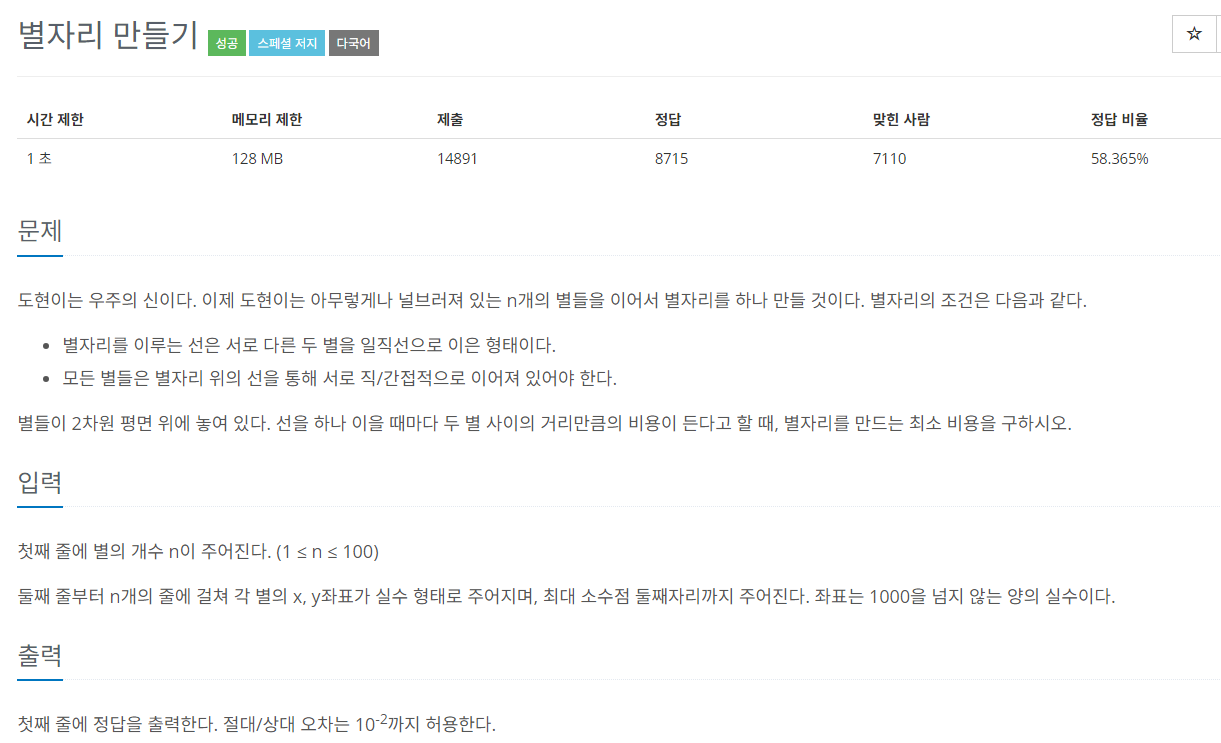
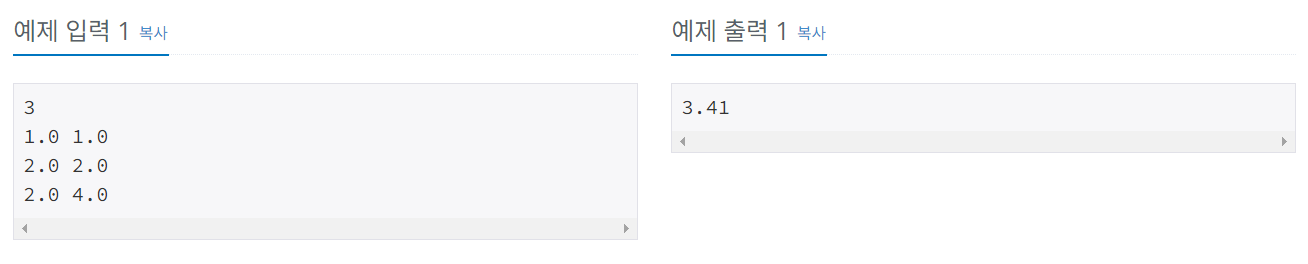
#1. 문제
#2. 풀이
2-1. 최소 신장 트리
[자료구조]#6_그래프
#0. 개념 1. 그래프? [정의] : 그래프는 노드와 간선들의 집합으로 이루어진 비 선형 자료구조입니다. 그래프의 노드들은 간선을 통해 연결되어 일종의 네트워크를 형성합니다. 그래프는 노드와
webddevys.tistory.com
Details
[개념] : 최소 신장 트리는 무방향 그래프 내 가중치의 합이 최소가 되는 최소 신장 트리입니다.
[특징] : 최소한의 간선, 최소 비용(최소 가중치의 합), 그리고 모든 정점 연결
[구현] : 크루스칼(Kruskal) 알고리즘, 프림(Prim) 알고리즘, 그리고 솔린(Sollin) 알고리즘
2-2. 크루스칼 알고리즘
크루스칼(Kruskal) 알고리즘은 MST를 구현하는 알고리즘 중 하나로, 그리디 알고리즘을 활용합니다. 크루스칼 알고리즘은 '간선 중심'의 MST 알고리즘으로, 간선 목록을 '가중치 기준' 오름차순 정렬하고, 정렬된 간선 목록을 순회하며 Union-Find 연산을 수행합니다. 이를 통해, 최종적으로 주어진 가중치 그래프로부터 MST를 구성합니다.
2-3. 프림 알고리즘
프림(Prim) 알고리즘은 MST를 구현하는 알고리즘 중 하나로, 그리디 알고리즘을 활용합니다. 프림 알고리즘은 '정점 중심'의 MST 알고리즘으로, 임의의 정점을 시작으로 어떤 정점의 '인접 정점'들을 순회하며 서로 연결된 간선 정보를 '가중치 기준 최소 힙(우선순위 큐)'에 삽입합니다. 이를 통해, 최종적으로 주어진 가중치 그래프로부터 MST를 구성합니다.
2-4. 솔린 알고리즘
솔린(Sollin) 알고리즘은 MST를 구성하는 알고리즘 중 하나로, 그리디 알고리즘을 활용합니다. 솔린 알고리즘은 '집합 중심'의 MST 알고리즘으로, 간선 목록을 순회하며 각 간선을 구성하는 시작 노드와 도착 노드가 속한 집합의 최소 가중치 간선을 찾고, 다시 각 집합의 최소 가중치 간선들을 모아놓은 데이터 목록을 순회하며 Union-Find 연산 수행 및 MST를 구성할 간선들을 추가합니다. 최종적으로, 가중치 그래프로부터 MST를 구성합니다.
2-5. MST 알고리즘 활용!
- 먼저, MST 알고리즘 중 하나를 활용합니다.
- MST 알고리즘 수행 과정에서 별도로 MST 목록에 추가될 간선들의 가중치의 합을 계산합니다.
#3. 코드
1. 크루스칼
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N;
// #1. 간선 구조체
struct Edge
{
int fromIdx, toIdx;
double weight;
Edge(int fromIdx, int toIdx, double weight)
{
this->fromIdx = fromIdx;
this->toIdx = toIdx;
this->weight = weight;
}
bool operator< (const Edge& other)
{
return weight < other.weight;
}
};
// #2. Union-Find 연산의 Find 연산
int Find(int x, vector<int>& parent)
{
if (parent[x] != x)
{
parent[x] = Find(parent[x], parent);
}
return parent[x];
}
// #3. Union-Find 연산의 Union 연산
void Union(int rootX, int rootY, vector<int>& parent, vector<int>& rank)
{
if (rank[rootX] > rank[rootY])
{
parent[rootY] = rootX;
}
else if (rank[rootX] < rank[rootY])
{
parent[rootX] = rootY;
}
else
{
parent[rootX] = rootY;
rank[rootY]++;
}
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N;
cout.precision(2);
cout << fixed;
vector<pair<double, double>> graph(N);
vector<Edge> edges;
// #1. 간선 목록 구성
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
{
cin >> graph[i].first >> graph[i].second;
// 간선 목록
for(int j=i-1; j>=0; --j)
{
// graph[i] 와 graph[j]의 거리 계산
double distance = sqrt(pow(graph[i].first - graph[j].first, 2)
+ pow(graph[i].second - graph[j].second, 2));
edges.push_back(Edge(i, j, distance));
edges.push_back(Edge(j, i, distance));
}
}
// #2. 크루스칼
// 부모 목록, 랭크 목록
vector<int> parent(N), rank(N, 0);
// 최종 최소 비용
double MSTWeight = 0;
// 부모 목록 초기화
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
parent[i] = i;
// 간선 목록을 가중치 기준 오름차순 정렬
sort(begin(edges), end(edges));
// 간선 목록 순회
for(const auto edge : edges)
{
// #1. Find 연산
int rootX = Find(edge.fromIdx, parent);
int rootY = Find(edge.toIdx, parent);
// #2. Union 연산 및 최소 비용 계산
if(rootX != rootY)
{
MSTWeight += edge.weight;
Union(rootX, rootY, parent, rank);
}
}
cout << MSTWeight;
return 0;
}2. 프림
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int N;
struct Node
{
double x, y;
};
double calculateDistance(Node& a, Node& b) {
return sqrt(pow(a.x - b.x, 2) + pow(a.y - b.y, 2));
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
// 소수점 밑으로 2자리까지 표현
cout.precision(2);
cout << fixed;
cin >> N;
// 그래프 선언
vector<Node> graph(N);
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
{
cin >> graph[i].x >> graph[i].y;
}
// 프림 알고리즘
vector<bool> visited(N, false);
double MSTWeight = 0;
// 우선순위 큐, pair< 가중치, 정점 인덱스 >
priority_queue<pair<double,int>, vector<pair<double,int>>, greater<pair<double,int>>> pq;
pq.push({0, 0});
while(!pq.empty())
{
int node = pq.top().second;
double weight = pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
if(visited[node])
continue;
visited[node] = true;
MSTWeight += weight;
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
{
if(!visited[i])
pq.push({calculateDistance(graph[node], graph[i]), i});
}
}
cout << MSTWeight;
return 0;
}
3. 솔린
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int N;
struct Edge
{
int fromIdx, toIdx;
double weight;
Edge(int fromIdx, int toIdx, double weight)
{
this->fromIdx = fromIdx;
this->toIdx = toIdx;
this->weight = weight;
}
};
// #3. Union-Find 연산의 Fin연산
int Find(int x, vector<int>& parent)
{
if (parent[x] != x)
{
parent[x] = Find(parent[x], parent);
}
return parent[x];
}
// #4. Union-Find 연산의 Union 연산
void Union(int rootX, int rootY, vector<int>& parent, vector<int>& rank)
{
if (rank[rootX] > rank[rootY])
{
parent[rootY] = rootX;
}
else if (rank[rootX] < rank[rootY])
{
parent[rootX] = rootY;
}
else
{
parent[rootX] = rootY;
rank[rootY]++;
}
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N;
// 소수점 아래 2자리 고정
cout.precision(2);
cout << fixed;
// 그래프 선언
vector<pair<double,double>> graph(N);
vector<Edge> edges;
// 그래프 구성
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
{
cin >> graph[i].first >> graph[i].second;
// 간선 목록
for(int j=i-1; j>=0; --j)
{
// graph[i] 와 graph[j]의 거리 계산
double distance = sqrt(pow(graph[i].first - graph[j].first, 2)
+ pow(graph[i].second - graph[j].second, 2));
edges.push_back(Edge(i, j, distance));
edges.push_back(Edge(j, i, distance));
}
}
// 솔린 알고리즘 수행
// 부모 목록, 랭크 목록
vector<int> parent(N), rank(N, 0);
int components = N;
vector<int> minWeights(edges.size());
double MSTWeight = 0;
// 부모 목록 초기화
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
parent[i] = i;
while(components > 1)
{
// 최소 가중치 목록 -1로 초기화
fill(begin(minWeights), end(minWeights), -1);
// 간선 목록 순회
for(int i=0; i<edges.size(); ++i)
{
// #1. from 과 to의 대표 노드
int comp1 = Find(edges[i].fromIdx, parent);
int comp2 = Find(edges[i].toIdx, parent);
if(comp1 == comp2)
continue;
// #2. 각 대표 노드의 최소 가중치 갱신
if(minWeights[comp1] == -1 || edges[minWeights[comp1]].weight > edges[i].weight)
minWeights[comp1] = i;
if(minWeights[comp2] == -1 || edges[minWeights[comp2]].weight > edges[i].weight)
minWeights[comp2] = i;
}
// #3. 최소 가중치 목록 순회
for(int i=0; i<minWeights.size(); ++i)
{
if(minWeights[i] != -1)
{
int comp1 = Find(edges[minWeights[i]].fromIdx, parent);
int comp2 = Find(edges[minWeights[i]].toIdx, parent);
if(comp1 == comp2)
continue;
// #4. 최소 신장 트리 비용 갱신
MSTWeight += edges[minWeights[i]].weight;
// #5. Union 연산
Union(comp1, comp2, parent, rank);
// #6. 집합 수 -1 차감
components--;
}
}
}
cout << MSTWeight;
return 0;
}
'문제 풀이 > BOJ 문제 풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ알고리즘, C++]#11404_플로이드, 플로이드-워셜, 최단 경로 알고리즘, 길 찾기 알고리즘 (1) | 2024.01.05 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ알고리즘, C++]#1647_도시 분할 계획, MST, 최소 신장 트리, 크루스칼, 프림, 솔린 (1) | 2023.12.21 |
| [BOJ알고리즘, C++]#2252_줄 세우기, 그래프, 위상 정렬 (0) | 2023.12.16 |
| [BOJ알고리즘, C++]#1753_최단 경로, 다익스트라 (0) | 2023.12.15 |
| [BOJ알고리즘, C++]#1922_네트워크 연결, MST, 최소 신장 트리, 크루스칼, 프림, 솔린 (0) | 2023.12.15 |
