[Basic C++] #49_STL 알고리즘, 불변 순차 알고리즘
STL 알고리즘 중 "불변 순차 알고리즘"에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
"전문가를 위한 C"의 17 항목, "STL 알고리즘 마스터하기"에 해당하는 내용입니다.
불변 순차 알고리즘
불변 순차 알고리즘은 "항목 열" 대상으로 동작하고, 원본 데이터에 변경을 가하지 않는 알고리즘을 의미합니다.
예를 들면, 어떤 항목 열의 범위 안에서 항목을 찾거나, 다른 항목 열의 범위와 비교하는 등 유틸리티 성격을 갖는 알고리즘들을 포함합니다.
검색 알고리즘
[Basic C++] #43_STL 알고리즘, find, find_if, accumulate
[Basic C++] #43_STL 알고리즘, find, find_if, accumulate STL 알고리즘 중 "find, find_if, accumulate"에 대해 알아보겠습니다. "전문가를 위한 C"의 17 항목, "STL 알고리즘 마스터하기"에 해당하는 내용..
webddevys.tistory.com
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v = { 5, 6, 9, 8, 8, 3 };
auto beginIt = cbegin(v);
auto endIt = cend(v);
// 1. find_if_not : Predicate 조건과 합치하지 않는 항목 찾기
auto it = find_if_not(beginIt, endIt, [](int num) {return num < 8; });
if (it != endIt)
cout << "First element greater than 8 is : " << *it << '\n';
// 2. minmax_element : 최소, 최대 항목 찾기
auto resPair = minmax_element(beginIt, endIt);
cout << "Min is : " << *(resPair.first) << " " << "Max is : " << *(resPair.second) << '\n';
// 3. adjacent_find : 같은 값을 인접한 항목들 중 첫 번째 항목
it = adjacent_find(beginIt, endIt);
if (it != endIt)
cout << "Adjacent consecutive value is : " << *it << '\n';
// 4. find_first_of : 두 값 중 어느 하나에 합치되는 첫 번째 항목
vector<int> v2 = { 8, 9 };
it = find_first_of(beginIt, endIt, cbegin(v2), cend(v2));
if (it != endIt)
cout << "Either found 8 or 9 ?" << "Yes!" << '\n';
// 5. search : 주어진 항목열과 합치하는 구간의 첫 번째 항목
vector<int> v3 = { 8, 3 };
it = search(beginIt, endIt, cbegin(v3), cend(v3));
if (it != endIt)
cout << "Found sequence of { 8 , 3 }" << '\n';
else
cout << "Couldn't find sequence of { 8, 3 }" << '\n';
}
비교 알고리즘
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
list<int> li{ 10, 20, 35, 40, 50 };
// bool equal( begin(a), end(a), begin(b))
if (li.size() == v.size() && equal(cbegin(v), cend(v), cbegin(li)))
{
cout << "The two containers have equal elements" << '\n';
}
else
{
// pair< First_mismatch_it , Second_mismatch_it> mismatch ( begin(a), end(a), begin(b) )
auto miss = mismatch(cbegin(v), cend(v), cbegin(li));
cout << "Following elements are equal : ";
for (auto it = cbegin(v); it != miss.first; ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << '\n';
cout << "Following elemets are not equal: ";
for (auto it = miss.first; it != cend(v); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
}
}* 결과 화면
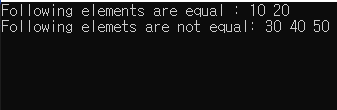
항목 열 간의 비교는 세 가지 알고리즘을 통해 가능합니다 - "eqaul()", "mismatch()", "lexicographical_compare()"
* 주의 : C++ 14부터 4개의 반복자 ( begin(a), end(a), begin(b), end(b) )가 가능합니다!
유틸리티 알고리즘
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10 };
// all_of( first_it, last_it, Predicate ) : 컨테이너의 모든 항목이 Predicate과 합치되는지 확인합니다.
if (all_of(cbegin(v), cend(v), [](int num)-> bool {return num == 10; }))
cout << "All Elements are 10!" << '\n';
else
cout << " Not All Elements are 10!" << '\n';
vector<int> v2{ 10, 10, 20, 10, 10 };
// any_of( first_it, last_it, Predicate ) : 컨테이너의 몇몇 항목이 Predicate과 합치되는지 확인합니다.
if (any_of(cbegin(v2), cend(v2), [](int num)->bool { return num == 20; }))
cout << "At least one element is 20!" << '\n';
else
cout << "No element which is 20!" << '\n';
vector<int> v3{ 50, 40, 30, 30, 20 };
// none_of( first_it, last_it, Predicate ) : 컨테이너의 모든 항목이 Predicate과 합치되지 않는지 확인합니다.
if (none_of(cbegin(v3), cend(v3), [](int i)->bool { return i == 20; }))
cout << "All Elements are not 20!" << '\n';
else
cout << "Some Elements are 20!" << '\n';
}* 결과 화면
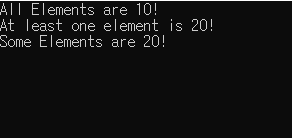
"불변" 유틸리티 알고리즘에는 "all_of()", "any_of()", "none_of()", "count()", 그리고 "count_if()"가 있습니다.
"count()"를 제외하면 모두 프레디킷을 활용한 제네릭 알고리즘입니다!
'언어 > Basic C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Basic C++] #51_STL 이동 알고리즘, move (0) | 2022.07.19 |
|---|---|
| [Basic C++] #50-1_STL 알고리즘, 변경 순차 알고리즘, transform(), copy(), copy_if(), copy_n() (0) | 2022.07.15 |
| [Basic C++] #48_함수 객체 어댑터, 바인더, not1(), not2(), mem_fn() (0) | 2022.07.09 |
| [Basic C++] #47_함수 객체 (0) | 2022.07.08 |
| [Basic C++] #46_람다 표현식과 STL 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.07.07 |
[Basic C++] #49_STL 알고리즘, 불변 순차 알고리즘
STL 알고리즘 중 "불변 순차 알고리즘"에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
"전문가를 위한 C"의 17 항목, "STL 알고리즘 마스터하기"에 해당하는 내용입니다.
불변 순차 알고리즘
불변 순차 알고리즘은 "항목 열" 대상으로 동작하고, 원본 데이터에 변경을 가하지 않는 알고리즘을 의미합니다.
예를 들면, 어떤 항목 열의 범위 안에서 항목을 찾거나, 다른 항목 열의 범위와 비교하는 등 유틸리티 성격을 갖는 알고리즘들을 포함합니다.
검색 알고리즘
[Basic C++] #43_STL 알고리즘, find, find_if, accumulate
[Basic C++] #43_STL 알고리즘, find, find_if, accumulate STL 알고리즘 중 "find, find_if, accumulate"에 대해 알아보겠습니다. "전문가를 위한 C"의 17 항목, "STL 알고리즘 마스터하기"에 해당하는 내용..
webddevys.tistory.com
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v = { 5, 6, 9, 8, 8, 3 };
auto beginIt = cbegin(v);
auto endIt = cend(v);
// 1. find_if_not : Predicate 조건과 합치하지 않는 항목 찾기
auto it = find_if_not(beginIt, endIt, [](int num) {return num < 8; });
if (it != endIt)
cout << "First element greater than 8 is : " << *it << '\n';
// 2. minmax_element : 최소, 최대 항목 찾기
auto resPair = minmax_element(beginIt, endIt);
cout << "Min is : " << *(resPair.first) << " " << "Max is : " << *(resPair.second) << '\n';
// 3. adjacent_find : 같은 값을 인접한 항목들 중 첫 번째 항목
it = adjacent_find(beginIt, endIt);
if (it != endIt)
cout << "Adjacent consecutive value is : " << *it << '\n';
// 4. find_first_of : 두 값 중 어느 하나에 합치되는 첫 번째 항목
vector<int> v2 = { 8, 9 };
it = find_first_of(beginIt, endIt, cbegin(v2), cend(v2));
if (it != endIt)
cout << "Either found 8 or 9 ?" << "Yes!" << '\n';
// 5. search : 주어진 항목열과 합치하는 구간의 첫 번째 항목
vector<int> v3 = { 8, 3 };
it = search(beginIt, endIt, cbegin(v3), cend(v3));
if (it != endIt)
cout << "Found sequence of { 8 , 3 }" << '\n';
else
cout << "Couldn't find sequence of { 8, 3 }" << '\n';
}
비교 알고리즘
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
list<int> li{ 10, 20, 35, 40, 50 };
// bool equal( begin(a), end(a), begin(b))
if (li.size() == v.size() && equal(cbegin(v), cend(v), cbegin(li)))
{
cout << "The two containers have equal elements" << '\n';
}
else
{
// pair< First_mismatch_it , Second_mismatch_it> mismatch ( begin(a), end(a), begin(b) )
auto miss = mismatch(cbegin(v), cend(v), cbegin(li));
cout << "Following elements are equal : ";
for (auto it = cbegin(v); it != miss.first; ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << '\n';
cout << "Following elemets are not equal: ";
for (auto it = miss.first; it != cend(v); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
}
}* 결과 화면

항목 열 간의 비교는 세 가지 알고리즘을 통해 가능합니다 - "eqaul()", "mismatch()", "lexicographical_compare()"
* 주의 : C++ 14부터 4개의 반복자 ( begin(a), end(a), begin(b), end(b) )가 가능합니다!
유틸리티 알고리즘
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10 };
// all_of( first_it, last_it, Predicate ) : 컨테이너의 모든 항목이 Predicate과 합치되는지 확인합니다.
if (all_of(cbegin(v), cend(v), [](int num)-> bool {return num == 10; }))
cout << "All Elements are 10!" << '\n';
else
cout << " Not All Elements are 10!" << '\n';
vector<int> v2{ 10, 10, 20, 10, 10 };
// any_of( first_it, last_it, Predicate ) : 컨테이너의 몇몇 항목이 Predicate과 합치되는지 확인합니다.
if (any_of(cbegin(v2), cend(v2), [](int num)->bool { return num == 20; }))
cout << "At least one element is 20!" << '\n';
else
cout << "No element which is 20!" << '\n';
vector<int> v3{ 50, 40, 30, 30, 20 };
// none_of( first_it, last_it, Predicate ) : 컨테이너의 모든 항목이 Predicate과 합치되지 않는지 확인합니다.
if (none_of(cbegin(v3), cend(v3), [](int i)->bool { return i == 20; }))
cout << "All Elements are not 20!" << '\n';
else
cout << "Some Elements are 20!" << '\n';
}* 결과 화면

"불변" 유틸리티 알고리즘에는 "all_of()", "any_of()", "none_of()", "count()", 그리고 "count_if()"가 있습니다.
"count()"를 제외하면 모두 프레디킷을 활용한 제네릭 알고리즘입니다!
'언어 > Basic C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Basic C++] #51_STL 이동 알고리즘, move (0) | 2022.07.19 |
|---|---|
| [Basic C++] #50-1_STL 알고리즘, 변경 순차 알고리즘, transform(), copy(), copy_if(), copy_n() (0) | 2022.07.15 |
| [Basic C++] #48_함수 객체 어댑터, 바인더, not1(), not2(), mem_fn() (0) | 2022.07.09 |
| [Basic C++] #47_함수 객체 (0) | 2022.07.08 |
| [Basic C++] #46_람다 표현식과 STL 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.07.07 |
